Top 10 Quality Management System Trends to Watch in 2025

Introduction
According to market analysis, the global quality management software industry is projected to exceed USD 15 billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of over 10%.
This rising curve reflects how crucial it has become for manufacturers to adopt quality management software solutions that are not just compliant but also agile, scalable, and intelligent.
The post-pandemic era triggered major operational shifts. Today, manufacturers are not only enhancing product quality but also reshaping their digital infrastructure with QMS system software that brings better traceability, reduced waste, and optimized performance.
A modern quality management system in manufacturing industry does far more than track defects — it supports continuous improvement, supplier collaboration, and strategic quality decisions across the entire value chain.
And in this transformation, 2025 is expected to be a pivotal year. Here’s a look at the QMS trends in the manufacturing industry that will shape quality strategies this year.
Emerging Quality Management Systems (QMS) Trends for 2025
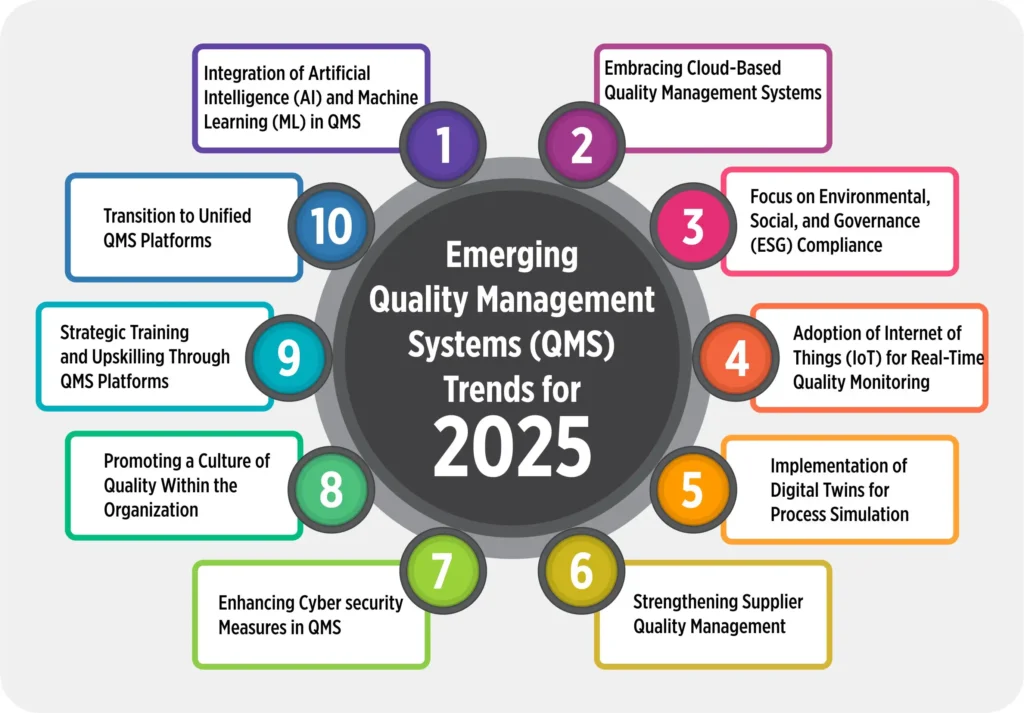
1. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in QMS
The incorporation of AI and ML into QMS is revolutionizing how manufacturers approach quality control.
These technologies facilitate predictive analytics, enabling organizations to anticipate defects before they occur and implement corrective actions proactively. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and anomalies that might elude human inspectors, thereby reducing the incidence of defects and rework.
This proactive approach not only enhances product quality but also leads to significant cost savings.
Moreover, AI-driven QMS solutions can automate routine tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. As AI and ML technologies continue to evolve, their integration into QMS will become increasingly sophisticated, offering even more robust tools for quality management.
2. Embracing Cloud-Based Quality Management Systems
The shift towards cloud-based QMS solutions is gaining momentum as manufacturers recognize the benefits of scalability, flexibility, and remote accessibility.
Cloud-based systems allow for real-time data sharing across multiple locations, facilitating better collaboration and faster decision-making. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with geographically dispersed operations.
These solutions come with lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premises systems and offer enhanced security features. As remote work becomes more prevalent, the ability to access QMS data from anywhere becomes a significant advantage, making cloud-based solutions essential for modern manufacturers.
Additionally, many manufacturers are turning to robust eQMS Software to manage documents, CAPAs, training, and audits — all within a secure, centralized cloud environment.
3. Focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Compliance
Sustainability and ethical practices are now central to quality management strategies. Manufacturers are integrating ESG metrics into their QMS to monitor and improve their environmental and social impact.
This includes tracking carbon emissions, ensuring fair labor practices, and maintaining transparency in sourcing and production. By embedding ESG considerations into their quality strategies, companies can enhance their reputation, meet regulatory requirements, and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Operational efficiencies gained through ESG compliance also result in cost savings and better risk management.
4. Adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) for Real-Time Quality Monitoring
IoT integration in manufacturing processes enables real-time data collection on equipment performance and product quality.
Sensors embedded in machinery detect deviations from standard operating conditions, allowing for immediate corrective actions. This reduces downtime, prevents defects, and enhances operational efficiency.
The data collected also supports trend analysis and continuous improvement, making IoT a vital component of smart, responsive quality management.
5. Implementation of Digital Twins for Process Simulation
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets or processes, allowing simulation and analysis without disrupting real operations.
Manufacturers can test different scenarios, identify potential issues, and optimize processes before implementation. This leads to more efficient and effective quality management with reduced trial-and-error costs.
By using digital twins, companies can ensure better process validation, improved product design, and minimized quality risks.
6. Strengthening Supplier Quality Management
With complex and globalized supply chains, managing supplier quality is increasingly important. Robust supplier quality management includes regular audits, performance evaluations, and improvement initiatives.
Ensuring suppliers meet high-quality standards maintains product consistency, reduces defects, and fosters reliable partnerships.
Clear communication of expectations and ongoing monitoring are key to effective supplier quality practices.
7. Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures in QMS
As digital QMS platforms store sensitive data, cybersecurity becomes critical. Manufacturers are investing in measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
Robust cybersecurity ensures data integrity, prevents breaches, and supports regulatory compliance. With the rise of digital transformation, secure QMS systems are a necessity.
8. Promoting a Culture of Quality Within the Organization
Quality isn’t just about systems—it’s about people. Embedding a culture of quality across the organization is essential for long-term success.
Modern QMS platforms support this by enabling better SOP adherence, real-time task tracking, and quality performance visibility.
When quality becomes a shared responsibility, outcomes improve at every level.
9. Strategic Training and Upskilling Through QMS Platforms
Training is key to consistent quality. In 2025, more organizations will use QMS software to track certifications, deliver digital learning, and assess employee readiness.
Effective training reduces human error, boosts SOP compliance, and builds a workforce that supports continuous improvement.
By investing in the right QMS system software today, manufacturers can unlock long-term advantages that go beyond compliance. Organizations that align quality processes with digital transformation are not only better equipped to adapt to change—they lead it.
10. Transition to Unified QMS Platforms
Disconnected tools create data silos and inefficiencies. Manufacturers are shifting to unified QMS solutions that bring together CAPA, non-conformance, audits, training, and document control.
Platforms like QualityPro offer integrated environments that streamline operations, improve communication, and enhance decision-making.
These platforms provide real-time access to reliable data, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned and informed.
Final Words
The QMS landscape is evolving rapidly. To remain competitive in 2025, manufacturers must align with these emerging trends and invest in future-ready solutions.
By leveraging technologies like AI, IoT, digital twins, and cloud-based platforms—and embedding ESG and quality culture into their strategies—companies can achieve operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
As manufacturers move toward unified systems, selecting the best QMS software for manufacturing becomes a strategic decision. Integrated platforms help ensure compliance, minimize risk, and provide a competitive edge in fast-paced markets.
In 2025, quality can no longer be an isolated department. It is deeply integrated with sustainability, cybersecurity, training, and data. Businesses that embrace this shift are building resilient, efficient, and trustworthy brands.
The future of manufacturing belongs to those who treat quality not as a checkbox, but as a strategic driver of growth. Those who implement a comprehensive, cloud-based, and AI-augmented QMS will reap the benefits of improved performance, stronger customer satisfaction, and sustainable success in a competitive market.