The Power of a Document Management System in the Pharmaceutical Industry

“If it’s not written down, then it didn’t happen”.
Considering the context of our blog topic, this proverb fits perfectly. In the pharmaceutical manufacturing, documentation acts as a mirror to show what’s actually happening within the company.
Moreover, every pharma company must follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Equally important is the adoption of Good Documentation Practices.
Documents play a pivotal role in establishing consistency across operations and minimize the risk of misinterpretations and errors in communication, thereby ensuring improved product quality.
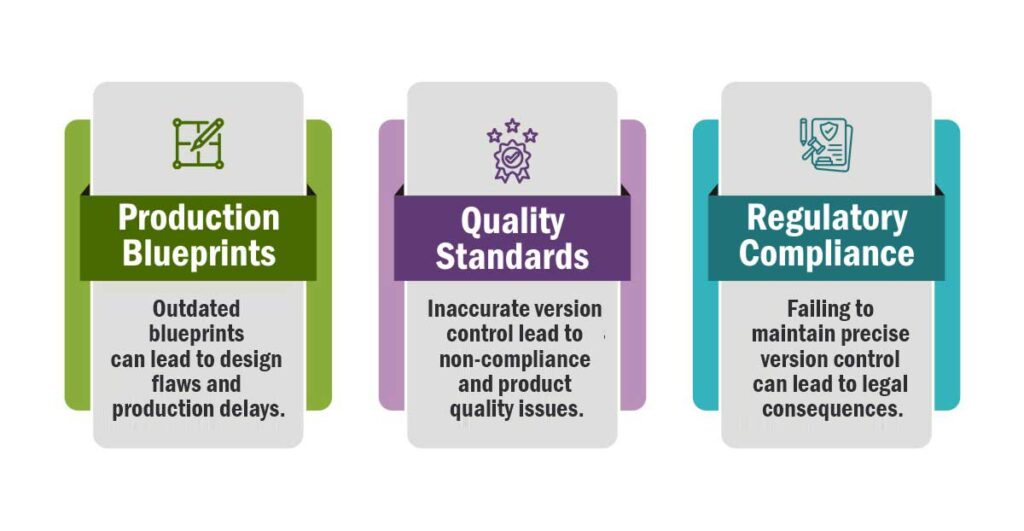
Adding to it is the need of managing hundreds may be thousands of formulas, both active and inactive along with their versions. Not to mention, regulatory bodies while inspecting a pharmaceutical manufacturing organization, precisely examines and validates all the documents and records, ensuring the processes, procedures, and products are adhering to the set industry standards, upholding the quality.
It is not overstating to say that in an industry like pharmaceuticals, where even a slightest error can have life-altering consequences for patients, documents act as the guardian of quality, safety, and compliance.
They act as the foundational stone for establishing quality management system in the pharmaceutical organizations.
However, a pharmaceutical manufacturing organization generates thousands of documents throughout the lifecycle of a product.
To manage such a huge volume of documents there should be a systematic and streamlined approach. And any system other than a document management system would succumb to errors and inefficiencies.
What is a Document Management System?
A document management system is defined as a systematic set of procedures and policies related to creating, capturing, storing, and tracking documents efficiently within an organization.
However, manual management of such a large volume of documents poses inherent risks and inefficiencies. Recognizing this, a crucial need for an automated document management software arises.
It eases the task of document management by providing a centralized, organized, and secured platform, enhancing efficiency of the tasks related to documents.
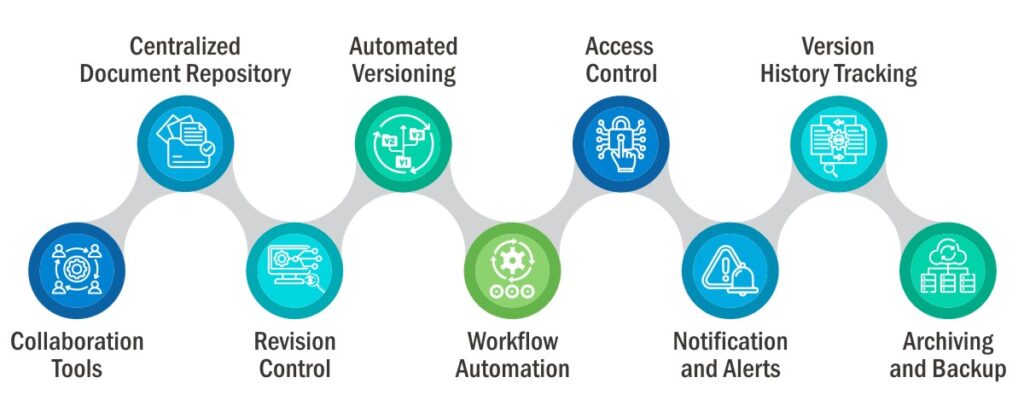
Features of an Effective Document Management Software-
An effective document management software encompasses a multitude of functionalities, elevating organizational convenience and streamlining operations.
Automating the Process of Document Management-
The software automates the complete document lifecycle right from creating to controlling, managing, organizing, and retrieving when required.
Moreover, it also manages multiple versions of documents separately, ensuring that only the Active version is being accessed by everyone.
Ensuring Timely Updates of Documents-
The software helps users to ensure that all the documents are up to date by providing alerts for expiry or whenever a document is due for revision/updates. It also sends notifications for release or pending approvals of documents.
Providing Easy Access to Crucial Documents-
By organizing all the documents at a centralized location, categorizing them based on file type, data type, and priority level, and allowing to search documents via metatags, a pharmaceutical document management software facilitates easy and quick access anytime, anywhere.
Ensuring Safety Through Access Control-
By enforcing access controls over the documents via passwords, a pharmaceutical document control software prevents from the risks of data theft or lost documents, ensuring tightened safety.
It also tracks all the activities performed on the documents, maintaining an audit trail of who and when viewed and modified the document.
Allows Effective Collaboration-
A robust pharmaceutical document management software enables such a capability that allows multiple people to collaborate and work on a common document without altering each other’s work.
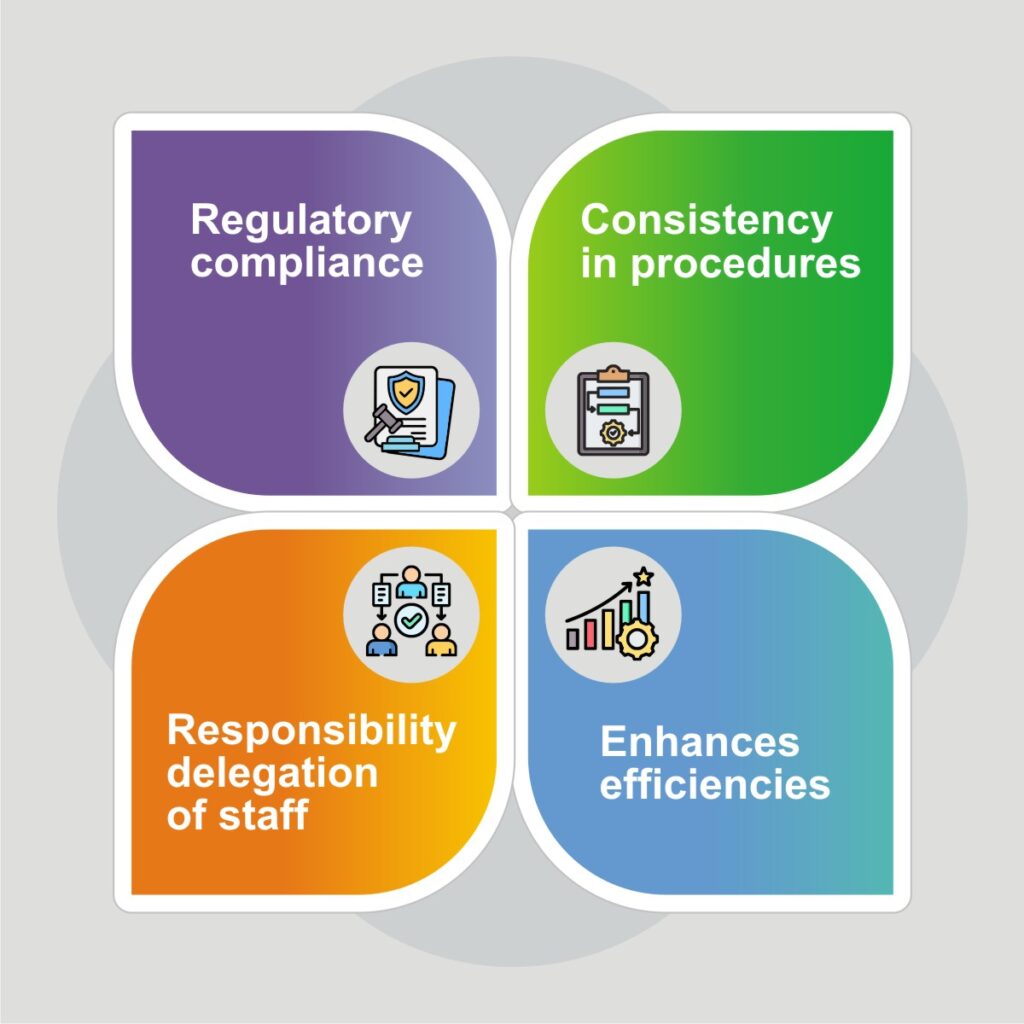
Benefits of a Document Management Software-
When a pharmaceutical organization implements such an effective and capable document management software, it experiences immense benefits on multiple business fronts-

Adherence to Compliance-
With an effective document management, a pharmaceutical organization will be audit-prepared every time with all the necessary regulatory documents, which will eventually lead to fewer compliance issues. This will even speed-up submitting documents for an Investigational New Drug Application.
Increased Operational Efficiency-
Today’s pharmaceutical industry demands an environment of agile decision-making and for this, critical documents accessibility plays a vital role. Enabling quick access to all the documents anywhere, anytime reduces the time usually spent on locating the required files, enhancing overall operational efficiency, and eliminating delays.
Maintains a Single Source of Truth-
By establishing a unified repository, a document management software for pharma industry ensures that all the stakeholders, researchers, and other employees access same information. This eliminates the risk of miscommunication between the departments that may arise when multiple documents are circulated.
Enhanced Security of Business Data-
Through role-based access, complete audit trail, and robust disaster recovery options, a document management software prevents loss or theft of data, ensuring high-end security.
Faster Time to Market-
A document management system (DMS) improves time-to-market by enhancing collaboration, ensuring version control, expediting approval processes, and facilitating quick document retrieval. With a centralized access to all documents of concepts and prototypes, automating workflows, and enhancing compliance management, a DMS accelerates the product development lifecycle, enabling faster delivery to market.
Final Thoughts-
Nowadays, pharmaceutical organizations that still relying on traditional (manual) practices of managing documents are likely to face a plethora of challenges.
So, implementing a document management software is the unavoidable need. However, choosing the right one is equally important for success. To your rescue come QualityPro’s Document Management System. It proves to be the perfect choice.
It is a comprehensive Quality Management Software with having robust and effective document management module that not only offers you the aforementioned functionalities, but it also allows easy integration with other quality related modules like Change Management, Standard Operating Procedures (SOP), Risk Management, Audit Management, Training management, Complaint Management, etc.