Best Practices of Quality Management for Electronic Industry

The rapid growth of the electronic market encompasses a vast array of products and components for diverse applications, including consumer electronics, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
In this ever-expanding industry, electronic manufacturers face constant pressure to deliver high-performance and reliable products.
To address these challenges and optimize their quality processes, implementing an advanced Quality Management System (QMS) can prove invaluable.
This system offers electronic manufacturers the means to address their concerns effectively and streamline their quality processes.
In the following sections, this blog will delve into the best practices of quality management specifically tailored for the electronics industry.
So, read on to discover how these practices can help electronic manufacturers navigate the evolving landscape successfully.
Overview-
The electronic industry is known for its rapid technological advancements, shorter product lifecycles, and high consumer expectations. In such a competitive landscape, maintaining high-quality standards and being cost-effective is crucial and can never be overlooked.
Even a well-reputed brand like Samsung was unable to maintain high-quality product standards. In the year 2016, it faced a widely publicized issue with its cellphone device – Galaxy Note 7 model.
The consumers experienced battery defects that caused the phone to overheat and, in some cases, caught fire. The company faced a lot of criticism and their brand value at that time degraded, leaving a bad impression on the loyal customers.
But wait, this isn’t just Samsung, we can list several other electronic companies that have earlier faced some or the other quality issues that made them experience brand defamation.
The only surefire way to stay out of situations like these is consistently delivering the best quality products in the market.
Products that comply with all the ever-changing norms and fulfill the customer’s demand. Because when their needs are met, they will be more satisfied with the products and unquestionably become brand loyal.
Implementing an efficient quality management solution and adopting its best practices simplifies maintaining excellent quality at all production stages for electronic device manufacturers.
What happens when the product’s quality is always at par?
When a product’s quality consistently meets or exceeds expectations, several positive outcomes can be observed:
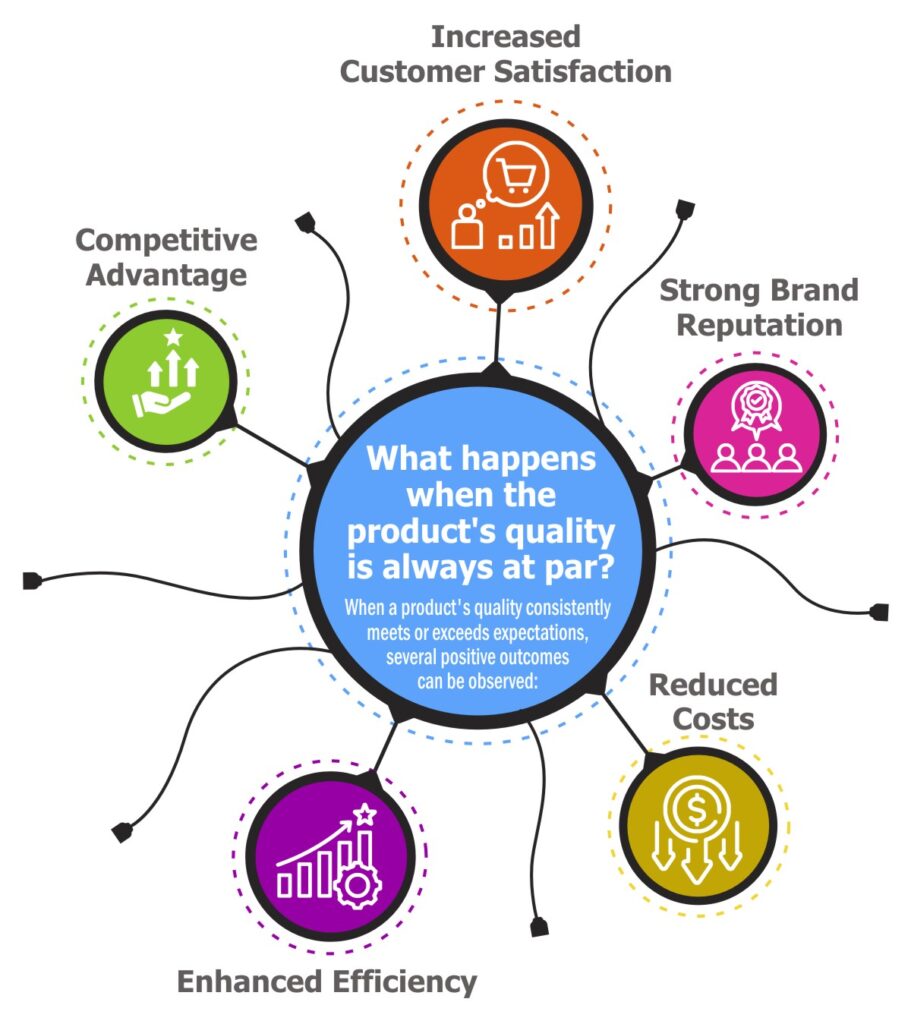
Increased Customer Satisfaction:
When a product consistently lives up to its quality promises, customers are more likely to be happy.
As a result, there is an increase in client loyalty, good word-of-mouth advertising, and the possibility of repeat business.
For example, when a smartphone consistently delivers excellent performance, meets user expectations, and provides a seamless user experience, customers are more likely to be satisfied.
They will appreciate the reliability, durability, and functionality of the product, leading to a positive overall experience, and thus a satisfied customer.
Strong Brand Reputation:
Consistently high-quality products contribute to building a strong brand reputation. A brand known for its superior quality gains trust and credibility among customers, leading to a competitive advantage in the market.
Apple is known for its high-quality products, and its brand reputation is built on delivering reliable and innovative devices. This reputation contributes to its strong loyal customer base, who are ready to never switch to android.
Reduced Costs:
Maintaining high product quality can result in substantial cost savings for the organization’s expenses in the long run. By minimizing defects, rework, and returns, they can avoid the expenses associated with fixing or replacing faulty products.
For example, an effective QMS system can help car manufacturers maintain strict quality control processes that can avoid costly recalls due to manufacturing defects, saving significant expenses on repairs and replacements.
Enhanced Efficiency:
Higher product quality means lesser customer complaints, reduced refund tickets, and repairs. Because of this, organizations can concentrate on other aspects such as innovation and growth, to improve the overall effectiveness of the business.
For example, a technology company can reduce the time and resources devoted to handling customer complaints and product issues by regularly delivering high-quality software updates and rapidly fixing security vulnerabilities.
Competitive Advantage:
Continuous delivery of excellent quality sets a brand apart from its competitors. It can have the capability to attract new customers who value reliability and performance and can also help in winning bids or securing partnerships in business-to-business relationships.
In a nutshell, when a product’s quality is maintained at a high level, both the company and its consumers benefit.
Best Practices of Quality Management for Electronic Industry

That said, electronic manufacturers must ensure following certain best practices that act as gateway to high quality. Here are some best practices that businesses should adopt to churn out the most from their business process and take their quality game to the next level:
Defining & Setting realistic quality goals –
To ensure consistent quality in electronic manufacturing, it is crucial to define and set realistic quality goals.
These goals should be documented, covering all production stages from component sourcing to final product testing. They should be measurable, achievable, and aligned with customer expectations and industry regulations.
Incorporating customer feedback and complying with relevant standards helps in refining and adapting the goals, while establishing measurable metrics enables progress tracking and performance evaluation.
Example: A company manufacturing smartphones may set a quality goal of producing mobile phones that have less than a 2% defect rate in their final products.
For this, they need to document the entire production cycle, determine the non-conformance and define actions to mitigate them.
Implementing Quality Control Measures:
To ensure that products fulfill the established quality standards, quality control measures should be implemented at every stage of the production process.
This comprises audits, multiple tests, and inspections at various phases, such as receiving raw materials, during manufacturing, and when they are being dispatched.
Continuous Improvement – An ongoing task:
To boost product quality and efficiency, regular activities such as evaluating processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing corrective and preventive actions should be done without fail.
Example: To find and address any flaws in their manufacturing process, a circuit board assembly company can regularly audit their processes and participate in ongoing training courses.
Implementing a quality management system (QMS)
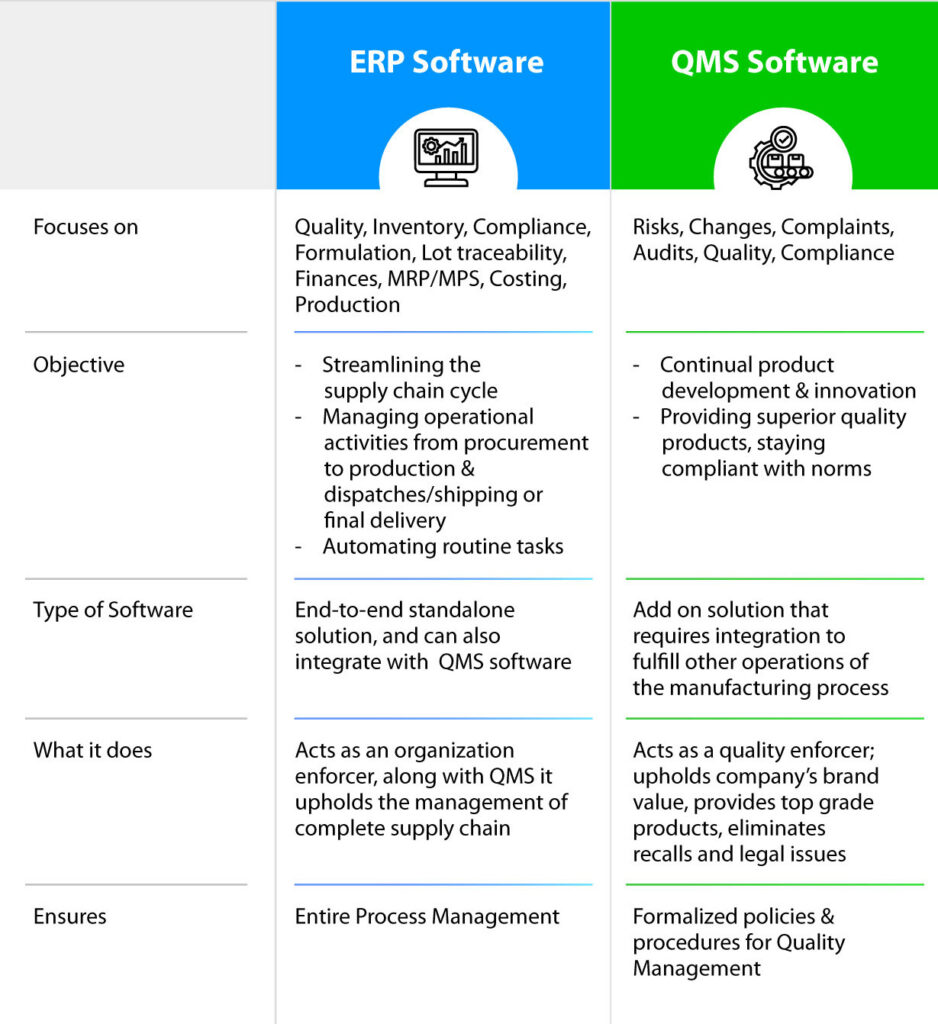
A tailor-made QMS system for the electronic industry will ensure that quality standards are consistently supported and the entire quality management process from start to finish is streamlined.
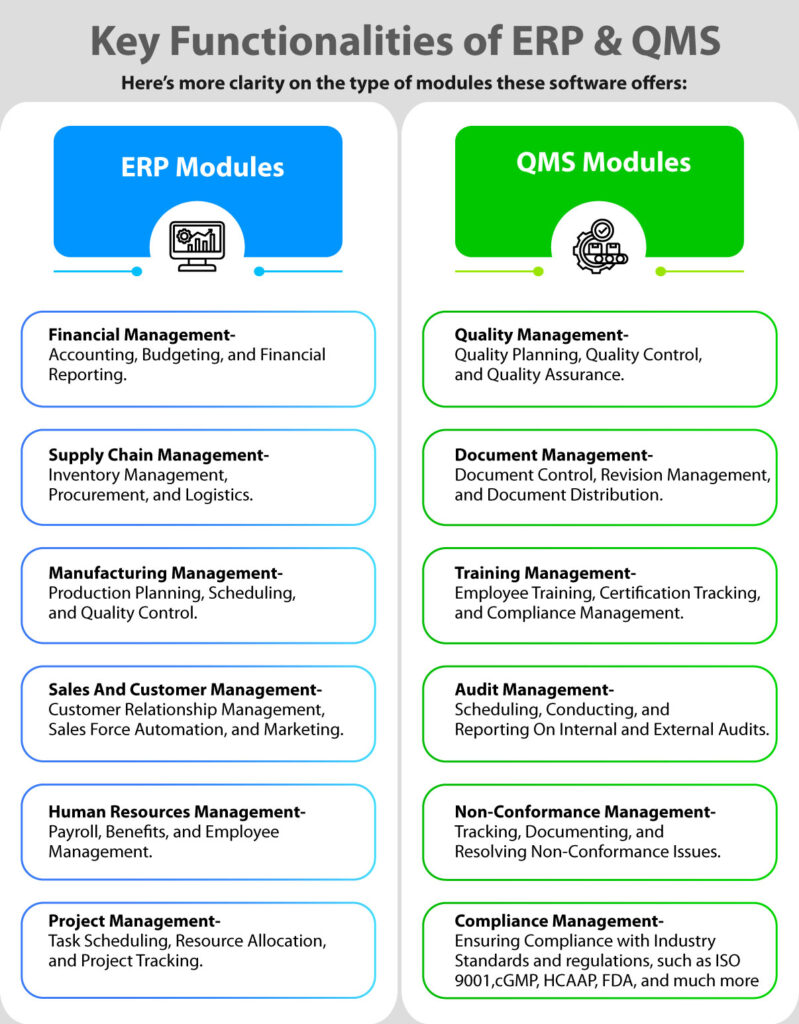
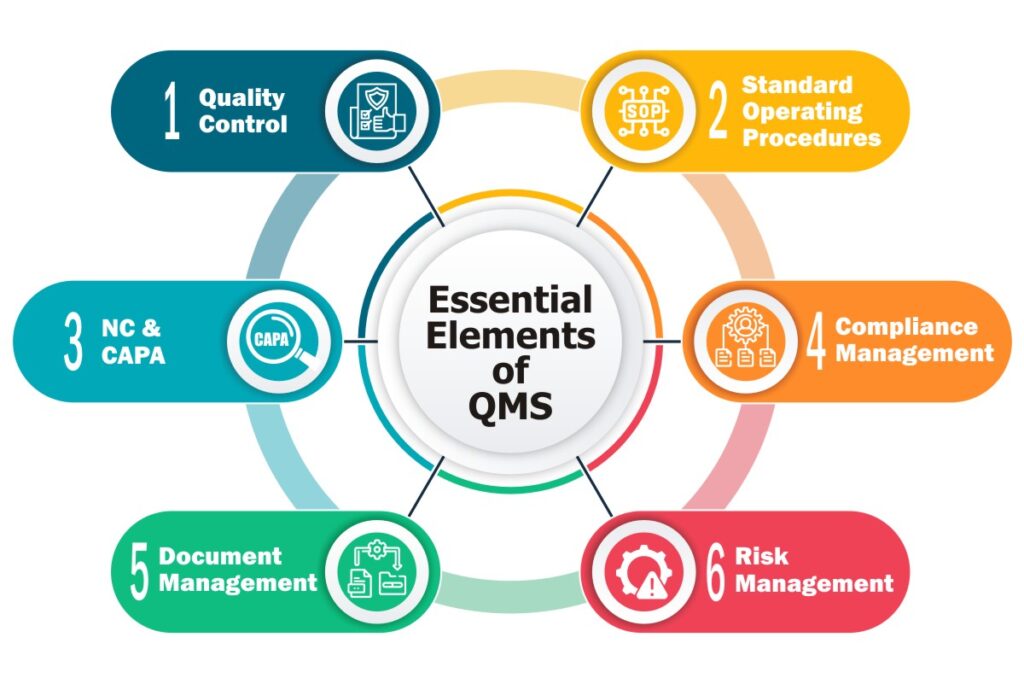
Modules like document management, process control, non-conformance management, and data analysis come under its umbrella.
Not only this, but it will also help in rectifying issues and fixing them to avoid future occurrences along with staying compliant with the norms. This way, the product’s quality becomes superior, and penalties or fines can be avoided.
A QMS software solution, for instance, can help the electronic manufacturing sector to centralize its quality-related documents, monitor quality KPIs, and automate workflows for increased productivity and compliance.
Supplier Quality Management:
Maintaining product quality depends on working with verified and reliable suppliers. It will be good practice for businesses to make sure that the components and materials they receive from suppliers meet the requirements.
This could be analyzed by conducting supplier audits and performance reviews. An electronics company, for instance, can periodically evaluate its suppliers based on factors including product quality, delivery effectiveness, and adherence to legal standards.
Continuous Training and Skill Development:
It’s important to provide employees with the chance to enhance their skills to maintain quality standards. Training in quality control methods, process improvement approaches, and maintaining up-to-date knowledge of industry rules are all part of this.
For example, a factory operator at an electronics company would benefit from training in quality standards, inspection methods, and the safe handling of delicate electronic components.
Summarizing thoughts on this,
Implementing effective quality management practices is essential for success in the fast-paced and cutthroat electronic sector.
Electronic manufacturers and suppliers can uphold high-quality standards, increase customer satisfaction, and build a strong brand reputation in the market by following regulatory requirements, managing suppliers effectively, implementing total quality management, controlling manufacturing processes, conducting extensive testing and validation, encouraging continuous improvement, engaging employees, and maintaining thorough documentation.
Adopting these best practices will aid the electronic industry’s long-term success and expansion. One quality expert that can help you in adhering to all of it is QualityPro.
This powerful, scalable, and robust TQMS software can help you instill a quality culture in your organization. So, get in touch with our experts now.