Things to Consider when Implementing a QMS System

Manufacturing companies use Quality Management Systems to identify faults in their processes and fix them by optimizing and standardizing them. This blog will guide you in comprehending the concept of quality management as well as the important things to consider for the implementation of QMS system.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Defining Quality Management System
- Result of a successful QMS implementation
- Things to consider when implementing a QMS System
- Summarizing thoughts
Overview
Businesses all around the globe are mounting their confidence in QMS systems to produce high-end quality products. They have recognized the need for an inclusive QMS software and are deploying it with the objective of enhancing the quality of their business processes, staying compliant with the stringent rules, and satisfying the customer demands. They, these days, are proactively assessing and investing in QMS solutions to ensure that quality standards are maintained at every stage of the product lifecycle.
Defining Quality Management System –
Before diving into the subject, here’ a quick brush-up on what a QMS essentially is-
Quality Management System (QMS) is a system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives. A QMS helps coordinate and direct an organization’s quality-related activities to meet customer and regulatory requirements and improve its effectiveness and efficiency on a continuous basis. Quality control systems are used by businesses to assess the quality of all factors involved in manufacturing and to ensure that the products or services meet their technical standards.
The implementation of a QMS system results in process improvement and standardization, as well as ensuring product and service quality.

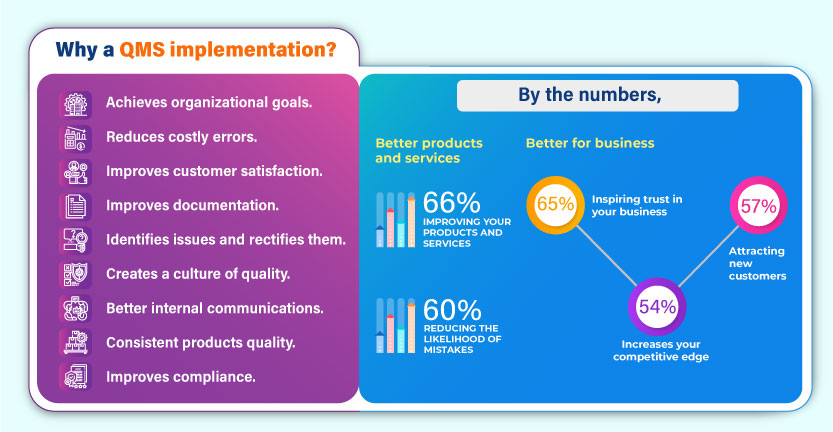
Why a QMS implementation?
- Achieves organizational goals.
- Reduces costly errors.
- Improves customer satisfaction.
- Improves documentation.
- Identifies issues and rectifies them.
- Creates a culture of quality.
- Better internal communications.
- Consistent products quality.
- Improves compliance.
Things to consider when implementing a QMS System –
Implementing a quality management system is not child’s play. It requires a huge amount of effort to put in. Companies need to take inputs from their staff members at all levels, right from the top management (the decision-maker) to the lower management. Once everyone gets on the same page, the aforementioned step should be followed for a QMS Implementation in manufacturing:
Need Analysis: A thorough analysis or an internal audit should be conducted. Companies should gather all the key business requirements and determine the software’s true need. They should calculate the anticipated risks and break down the important areas that will give significant consumer satisfaction. It will give businesses a good understanding of where the current procedures are lagging and what the new system will do.
Planning: Make a list of the gaps in the current processes based on the analysis of the quality management processes. It will enable companies to go on to the next step of gathering resources and establishing an effective implementation strategy. Divide the project into sub projects and assign a deadline for each. Put up a team that monitors if the implementation progress takes place in the specified time frames or not. Any delays should be brought to the notice of top management and should be accounted for.
Bringing team & stakeholders on the same page: Ensure that all the employees from the top to the bottom are involved in the project. They should know about the new system. Furthermore, all stakeholders should be trained on using the new system.
Teamwork: Form a team to deal with the issues related to the software. It should be composed of people from several departments, with someone in charge, ideally from the quality or IT departments.
Selecting the system: Select the appropriate solution after articulating the needs, and search for key business-critical variables. Know about frequent updates, vendor support in terms of training and maintenance, etc.
Deployment phase: Deploy the system and validate that it is compatible with all existing business systems and that it has been configured to meet specific needs. Collecting and migrating existing data to the software’s database is also done at this stage.
Control & Measure: Set some benchmarks for evaluating the new system’s performance. Define the procedures for controlling, measuring, and monitoring outputs to verify that they satisfy quality standards.
Review process for continuous improvement: Schedule product or process audits to ensure that policies and requirements are met. Companies should continue to audit and assess the procedures on a regular basis to ensure that they are evolving.
Summarizing thoughts:
By following the steps mentioned above, businesses can implement an effective QMS system. Contact us to know about an expert partner who can assist you with the implementation of quality management system in manufacturing. Our in-house quality experts at QualityPro will be pleased to help you.