‘Complexity’ is one term that is omnipresent in every stage of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The entire process—from choosing raw materials to processing them in a controlled environment, packaging without sacrificing quality, and delivering the products—must comply with stringent regulatory standards.
Adding a layer to this complexity is the occurrence of any change. Change may be in the process, documentation, machinery, facility, vendor, or any other. Any change brings an array of adjustments, a torrent of confusion and the risk of quality deterioration.
Here comes the importance of change control in the pharmaceutical industry. It acts as a shock absorber on the bumpy road of the pharmaceutical business. We’ll dig deep into the importance of change control, but first, let’s understand it better.
What is Change Control in Pharma?
Change control in pharma is a systematic process that involves careful evaluation, documentation, and approval of changes to pharmaceutical processes, equipment, facilities, suppliers, documents, change management system, SOPs, and even personnel.
Change control intends to minimize risk and ensures that any change is smooth throughout the organization without negatively affecting the quality, efficacy and safety of the products. Moreover, change control ensures that the outcome is as compliant as its predecessor.
Generally, changes occur in the following areas:
Production
- Change in location
- Change in equipment
- Change in batch size
Engineering
- Change in equipment
- Change in facility area
- Change in part of equipment
R&D
- Change in specification of raw materials
- Addition/deletion of raw materials in the product
- Change in quantity of raw materials in a product
- Change in shelf life
- Change in environmental conditions
- Change in storage conditions
- Change in stability protocols
Quality Control
- Change in method of analysis
- Change in hardware /software of the analytical instrument
- Change in stability protocols
- Change in specification of in-process/ intermediate materials
Quality Assurance
- Change in the sampling plan
- Change in documentation/SOPs
- Change in the validation process
Cleaning process
- Change in cleaning steps
- Change in cleaning aids
- Change in cleaning agents
The above list is just suggestive and not exhaustive. The list is mentioned to give you a fair idea of the scope of changes in the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry.
Cycle of Change Control:
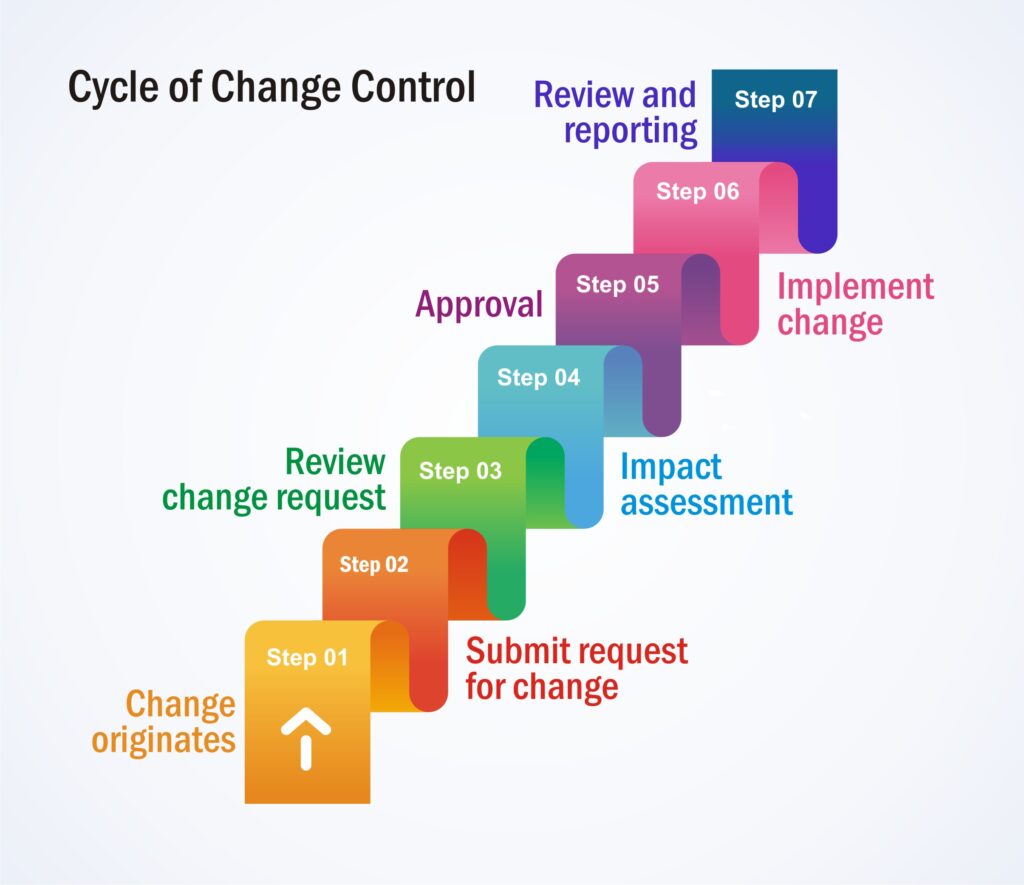
- Step 1– Change originates
- Step 2– Submit a request for change
- Step 3– Review the change request
- Step 4– Impact assessment
- Step 5– Approval
- Step 6– Implement change
- Step 7– Review and reporting
Types of Changes:
Changes are broadly divided into two groups:
Unplanned Change:
Any unexpected modification that requires immediate action is termed as Unplanned Change. These are generally the result of any unforeseen event, like equipment failure, deviation from set procedures, etc.
Planned Change:
An intentional and pre-defined change or modification that is implemented with proper evaluation and authorization falls under the category of Planned Change. These changes are carefully considered, and every dimension of safety, efficacy, and quality is assessed before implementation.
Importance of Change Control in the Pharma Industry:

On a macro level, change control is important to pave a smooth path for change in the organization. It ensures that changes don’t trigger quality loss, safety threats, or efficacy deterioration.
Let us broaden the lens and see the importance of change control in the pharmaceutical industry.
Regulatory Compliance:
Pharmaceutical manufacturing organizations must adhere to various national and international compliance norms set by regulatory bodies like FDA, EMA, DHA, CDSCO, MHRA, etc.
Change control ensures that the organizations meet the guidelines laid by these bodies and adhere to cGMP (Good Manufacturing Practices).
For example: When the need for a change arises, it is first evaluated and approved. A proper plan is devised and concerned stakeholders are informed about the change. The whole process is documented and the documents in respective departments are also modified accordingly.
Thus, the whole process ensures transparency, and accountability besides fulfilling the documentation requirements necessary for regulatory compliance.
Risk Management:
Change control helps in mitigating risk in advance. By proactively evaluating the impact of the proposed change, it can foresee the risks. This foresightedness can help manage risks with due care and dampen their impact on the organization.
Documentation and Accountability:
Meticulous documentation of all changes is the key process involved in change control. Additionally, it involves documentation of the rationale behind the change and decisions made throughout the evaluation process.
The whole documentation serves as a transparent record for various regulatory requirements. These documents identify the approving authority, fostering accountability within the organization.
Continual Improvement:
Improvement is at the core of any proposed change in an organization. This improvement can be in the processes, manpower, equipment, or any other.
Change control helps to bring improvement in a regulated and systematic fashion within pharmaceutical organizations.
For example, if a pharmaceutical organization upgrades a tablet coating machine, it does so with the intention of offering better precision and efficiency.
Change control not only results in an upgraded machine, but it also affects (improves) the overall processes related to a new machine’s upgrade such as its working procedure, material required, lead time, resources, SOP, and so on.
Product Consistency:
Change control aids in maintaining product quality and consistency. Pharmaceutical manufacturing is critical, and even a slight change can deviate the final product from the set standard.
By implementing a robust change control system, organizations can ensure that every change is evaluated, documented, and tested to maintain product consistency.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings:
By managing changes systematically, organizations can avoid downtime or production delays. Change management can also help avoid regulatory penalties and product recalls, thereby protecting the company’s image and financial health.
Better Communication and Coordination:
A change control system promotes communication and collaboration among various departments of the organization. It ensures that every department is aware of the change, its impact, and implementation strategies.
If the need arises, departments can raise issues, suggest alternatives, or voice their apprehensions to foster better communication and coordination within the organization for improved decision-making.
These are some of the important functions of change control in any pharmaceutical industry. Let us now take a bird’s eye view over ideal practices to make the change control effective.
Best Practices for Effective Change Control
To implement an effective change control process, pharmaceutical companies should consider the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Procedures
- Involve Key Stakeholders
- Conduct Thorough Impact Assessments
- Maintain Detailed Documentation
- Review and Approve Changes
- Monitor and Review Changes Post-Implementation
While adopting these best practices is crucial, leveraging technology can further enhance the efficiency and accuracy of change control management.
Role of QMS Software in Streamlining Change Control Management:
Traditionally, change control is done manually using paper-based systems, leading to errors, repeated work, and delays in updating everyone involved.
An Electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) offering built-in support for change control is the key. Change Control management software can digitize the entire change process and centralize all the information in one system.
The system helps record, manage, review, verify, validate, approve, and update the change to all stakeholders thereby meeting compliance.
Key Functionalities of the Change Control System are:
- Change Request Initiation: Initiate and document change requests for processes, documents, or systems.
- Impact Evaluation: The module evaluates the potential effects of changes on processes, compliance, and operations.
- Automated Workflow: It automates the entire change management process, from request initiation to implementation and closure.
- Cost measurement: Evaluate the proposed change by measuring the costs associated with the change.
- Compliance Assurance: It ensures adherence to regulatory standards by maintaining a detailed audit trail for all changes.
- Collaboration and Communication: Help Identify departments affected by the change intimating them of the same through alerts & notifications.
- Documentation: Maintains a centralized repository for all change-related documentation.
- Verification and Closure: Ensures changes are verified post-implementation for effectiveness before closure.
- Training on Changes: identifies who needs to be trained for the change and schedules the training on same.
If you are a pharmaceutical organization, looking forward to injecting electronic capabilities of change control, then QualityPro QMS for pharmaceutical is software you should look forward to.
To know more about it, write to us at sales@tecwrk.com.





